This article will explain how California's cost of electric vehicles compares to other energy sources. It covers issues such as the cost of supporting electric vehicles (EVs) and the reliability of the grid. It also covers the state's goals for clean energy. You'll also learn the advantages and disadvantages EVs have, and how you can improve the grid.
California's clean energy goals
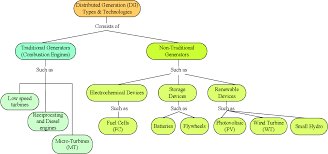
California's clean energy goals aim to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Despite our clean energy goals, the state still uses fossil fuels to meet our energy needs. The state ranks 14th in natural and oil production. We would be able to reach our goal of 100% renewable energy by 2045 if we adopt the state's clean-energy goals.
California still has a ways to go before we can achieve these goals. But, there are some steps that are already being taken. One of those steps is to make more use of distributed, renewable energy sources. California has made significant investments in renewable energy resources and solar energy in recent years. The state intends to generate half its power from renewable resources by 2025. While lawmakers work on legislation to speed up the transition to cleaner energy, they are also drafting legislation. More than 25 bills are currently pending in the state legislature.

Increased reliance on renewable resources
California is making great strides in increasing the use of renewable energy. Renewable energy accounted for 19.8% of California's total electricity generation in 2013. This number is expected rise to 35% in 2030. This growth will be mostly due to solar and wind power, but non-hydro energy sources have grown from a mere 1% in 2005 down to 12.5% by 2020. However, the demand for electricity remains relatively stable. The use of renewable fuels for transportation has increased significantly over the past few years, going from a mere 1% rate in 2005 to nearly double that last year.
California passed the Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) to encourage more renewable energy. This act requires electricity providers to purchase renewable energy to meet their renewable electricity needs. This law requires that utilities buy at least 20% renewable electricity by 2022. Furthermore, they must increase their renewable portion by 1% each year.
Supporting EVs - Costs
California's Air Resources Board plans to spend $95 Million on various EV projects by the end 2019. The money comes from a portion from registration fees, and proceeds from cap & trade programs. The program is expected offer rebates to EV-owners. You should, however, consider the price of an EV before you decide to buy one.
California's largest utilities offer two types EV charging rates. The first rate only applies to electricity consumed by EVs. The second rate covers all electricity consumed by a house.
Grid reliability
California's grid reliability is a problem that has been concerning for a long time. The state is dependent on external power for 20 percent to 30% of its electricity. This leaves its grid vulnerable to weather changes and political developments. The electricity grid is being put under extreme strain by the increasing demand for energy and electric cars.
State efforts are being made to improve grid reliability. Recently, the Board of Governors of California Independent System Operator approved four new reliability must-run power plant contracts. These contracts will ensure that power plants will continue to run throughout the duration of the agreements, which extend to calendar year 2023.